In today’s era of technological development, the need to expand wifi network coverage is increasing, especially in large spaces like homes, offices, or coffee shops. Connecting multiple wifi routers at the same time is the optimal solution to improve speed, minimize signal interference, and provide the best network experience. In this article, Genfarmer will explore the detailed steps to set up an effective and stable network system by connecting multiple wifi routers.
Benefits of connecting multiple wifi routers

Connecting multiple WiFi routers is an effective solution that helps optimize the Internet network, expand coverage, and improve user experience. Below are the outstanding benefits of using a connection of multiple WiFi routers.
Expand WiFi coverage
The biggest benefit of connecting multiple WiFi routers is the ability to expand coverage. For multi-story houses, large offices, or areas with many dead spots, the WiFi signal often cannot cover the entire area. Adding secondary routers helps the signal spread evenly, ensuring all devices in the space can connect to the Internet easily and stably.
Improve network speed and stability
When many devices connect to a single router, the network often becomes overloaded, leading to reduced access speed and lagging. Using multiple routers helps distribute the traffic, reducing the load on each router, thereby improving the network’s speed and stability. Users can enjoy a smoother experience, even when streaming 4K videos, playing online games, or participating in online conferences.
Suitable for smart homes and a large number of devices
Nowadays, modern families often use many smart devices such as lights, speakers, security cameras, or IoT devices. A single router is often not enough to meet the needs of this increasing number of devices. Connecting multiple routers helps create separate access points, ensuring each device operates stably and minimizing the risk of disruption.
Easy to manage and upgrade the network
Using multiple routers not only brings technical efficiency but also makes network management more flexible. Users can set up sub-networks for each area or for different purposes, such as a separate network for guests or a home office. Besides, when an upgrade is needed, you only need to replace or add a specific router without affecting the entire system.
Enhanced security
Another important benefit of connecting multiple routers is the ability to enhance security. You can set up a separate network for guests or IoT devices to limit the risk of unauthorized access to the main network. This is particularly useful for protecting personal data or sensitive business information, while minimizing the risk of cyber attacks.
Cost-effective solution
Instead of investing in high-end WiFi systems or expensive mesh networks, connecting multiple wifi routers is a cost-effective solution that still delivers high performance. You can utilize old routers as secondary access points, reducing purchasing costs. Additionally, this method helps avoid wasting resources and optimizes the performance of the current network system.
Detailed guide to connecting multiple wifi routers
In today’s technological age, expanding wifi coverage in a home or office is a common need. To achieve this, you can use a connection of multiple WiFi routers. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to do this.
Step 1: Set up the IP range
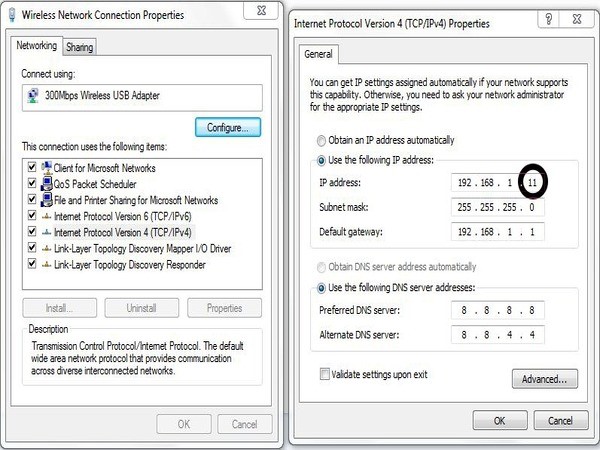
First, you need to ensure that each wifi router in your system uses a different IP range to avoid conflicts. For example, if the main router uses the IP range 192.168.1.x, then the second router can be configured to use the IP range 192.168.2.x. Access the admin page of each router to make this adjustment.
Step 2: Secure the IP address

After setting up the IP range, the next step is to secure the network’s IP address. Make sure you have enabled the firewall and are using other security features supported by the router, such as MAC address filtering, disabling DHCP if not necessary, or setting a strong password for the wifi network.
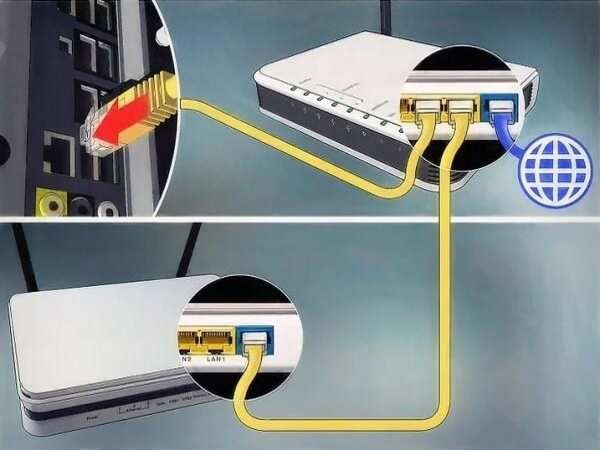
Step 3: Connect the wifi

After completing the steps above, you can proceed to connect the routers. The simplest way is to use a network cable to connect the LAN port of the main router to the LAN port of the secondary router. Alternatively, you can also use the wireless connection (WDS) feature if the routers support it.
Step 4: Access the wifi router’s IP address

After completing the physical connection, you need to access the IP address of each router to check the settings. Using a web browser, enter the router’s IP address into the address bar to access the admin page.
Step 5: Fill in the login information

When you successfully access the admin interface, the system will ask you to enter your login information. Typically, the default information is written on the back of the router or in the user manual. Be sure to change the default password to ensure security.
Step 6: Complete the connection of the wifi routers

Finally, recheck the entire connection and ensure that all routers are working well. Try connecting devices to the wifi network to test the speed and stability. If everything is fine, you have successfully completed the task of connecting multiple wifi routers.
Some simple terminology

When performing network setups or configurations, especially when connecting multiple wifi routers, you will often encounter some technical terms. Below are detailed and easy-to-understand explanations of common terms:
- Router: A router is a network device used to connect multiple devices within a local area network (LAN) and to direct data between the local network and the Internet. It acts as a “coordinator,” ensuring that data is sent to the correct place and device.
- IP Address: An IP address is a series of numbers used to identify devices on a network. Each device on the network has a unique IP address, which helps the router know which device needs to send or receive data. For example, a common IP address is 192.168.1.1.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): DHCP is a protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. When a device connects to the network, the router uses DHCP to provide an available IP address for that device without manual configuration.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): The SSID is the name of the wifi network that you usually see when searching for wifi connections. This is how you distinguish your wifi network from others in the area.
- WDS (Wireless Distribution System): WDS is a feature that allows you to connect multiple wifi routers together without cables. This is useful when you want to extend wifi coverage in your home or office.
- LAN (Local Area Network): A LAN is a local network that connects devices within a small area, such as a home, office, or school. A LAN is set up through the router’s LAN ports.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): A WAN is a wide area network that connects smaller networks (LANs) to the Internet. The WAN port on a router is typically used to connect to the Internet modem.
- Modem: A modem is a device that converts the signal from the Internet service provider (ISP) into a signal that the router can use to create a wifi or LAN network.
- Frequency Band: The frequency band is the frequency at which a wifi network operates. Currently, the two most common bands are 2.4GHz and 5GHz. The 2.4GHz band has a wider coverage range but lower speed, while the 5GHz band has higher speed but a shorter range.
Mastering these terms will help you easily perform network setups, troubleshoot issues, and optimize your network’s performance. Even if you are not a tech expert, understanding these basic concepts will bring convenience and confidence in managing your network.
Notes when connecting multiple wifi routers
Connecting multiple wifi routers is an optimal solution to extend network range and improve connection quality in large spaces. However, if not done correctly, you may encounter issues such as signal interference, IP conflicts, or unstable network speeds. Here are important notes to ensure the network system operates effectively.
Choose the right role for the routers
For the network to operate stably, assigning roles to the routers is very important. The main router will connect directly to the Internet modem, responsible for assigning IP addresses and managing network traffic. Secondary routers should only be configured to extend the network, using “Access Point” or “Bridge Mode” to avoid conflicts with the main router. This helps ensure synchronization and efficiency in the network system.
Ensure a stable connection between routers
The connection between routers can be made via an Ethernet cable or a wireless connection (WDS). A wired connection is always the most stable option as it is not affected by interference. If using WDS, you need to place the routers in a reasonable position to ensure the signal is not degraded. Check the network cables and devices carefully to avoid connection errors.
Set up SSID and wifi password
The SSID is the name of the wifi network you see when searching for a connection. You can use the same SSID and password for all routers so that devices automatically switch as they move around the house. However, if you need to differentiate the networks, you can set different SSIDs. Ensure the wifi password is strong, using letters, numbers, and special characters to enhance security.
Choose the appropriate frequency band
If your router supports dual-band (2.4GHz and 5GHz), configure it to suit your usage needs. The 2.4GHz band has a wider coverage range but lower speed, while the 5GHz band provides high speed but a shorter range. Also, adjust the wifi channel to avoid interference with neighboring networks.
Check network speed and performance
After setup, you should check the network speed and performance in different areas of the usage space. Use tools like Speedtest to measure download speed, upload speed, and latency (ping). If you find an area with a weak signal, you can adjust the router’s position or add supporting devices like a repeater or mesh wifi.
Update firmware for the router
Firmware is the software that controls the router’s operation. To ensure performance and security, regularly check for and update the firmware from the manufacturer. New versions not only fix bugs in the system but also provide new features, helping to enhance the network’s performance.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly implementing the process of connecting multiple wifi routers at the same time will help you expand your network range, improve connection performance, and minimize issues during use. With the detailed instructions above, you can easily set up a stable and fast network system, serving the needs of your family, office, or other large spaces well. Always remember to check and optimize your settings to achieve the best results.











