Imagine the internet as a colossal, sprawling city. Every website, server, and online service is a unique destination—a house, a library, a massive corporate headquarters. To navigate this digital metropolis, you need an address. But while we humans prefer memorable names like “genfarmer.com,” computers communicate using strings of numbers called IP addresses. So, how does your browser find the correct numerical address when you type in a simple website name? The answer lies in an invisible, yet indispensable, system working tirelessly behind the scenes: the Domain Name System (DNS). Understanding this system isn’t just for IT professionals; it’s fundamental knowledge for anyone in digital marketing, MMO, or business automation who relies on the seamless connectivity of the web.
What is DNS? The Internet’s Grand Directory
At its core, the Domain Name System (DNS) is the “phone book” of the internet. Its primary, and most critical, function is to translate human-readable domain names (like genfarmer.com) into the numerical IP (Internet Protocol) addresses (like 192.0.2.1) that computers use to identify and locate each other on the network. Without DNS, the internet as we know it would be unusable.
Think about it: could you imagine having to memorize 172.217.14.228 to visit Google or 104.18.20.187 for another favorite site? It’s simply not practical. Humans are good at remembering names, not long sequences of numbers. DNS bridges this gap, acting as a massive, distributed database that maps names to numbers. When you enter a URL into your browser, you are initiating a DNS query, essentially asking, “What is the IP address for this website?” This process, known as DNS resolution, is the first step in every single online interaction, from loading a webpage to sending an email.

The DNS Resolution Process Simplified: A Journey from Name to Number
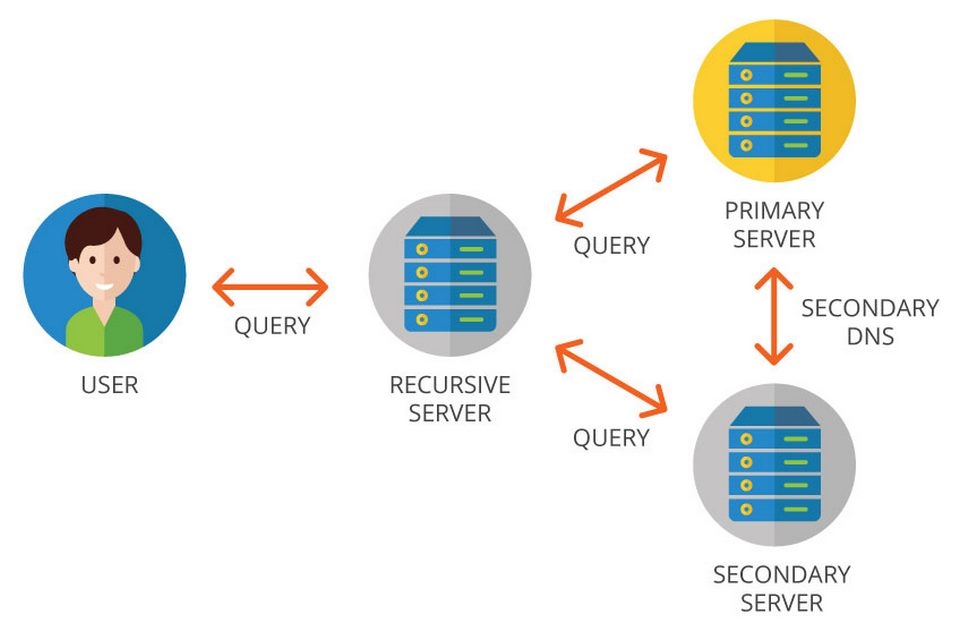
The journey of a DNS request is a marvel of speed and efficiency, involving a hierarchical chain of servers that work together to find the correct IP address. The entire process often takes mere milliseconds. Let’s walk through a simplified version of what happens when you type genfarmer.com into your browser and hit Enter.
- The User’s Request: You type the domain name into your web browser. The browser and your operating system first check their own local cache to see if they’ve visited this site recently. If the IP address is stored locally, the process jumps to the end. If not, the query begins its journey.
- The Recursive Resolver: Your computer sends the query to a special server called a DNS recursive resolver (or recursive DNS server). This server is usually operated by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Its job is to find the correct IP address on your behalf. It’s like a persistent librarian who will search every index until they find the book you need.
- Querying the Root Servers: If the recursive resolver doesn’t have the IP address in its cache, it contacts one of the 13 root name servers that are strategically placed around the globe. These root servers don’t know the IP address for
genfarmer.com, but they know where to find the servers that manage all.comdomains. They respond by directing the resolver to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) name server. - Querying the TLD Name Servers: The recursive resolver then sends the query to the TLD name server for
.comdomains. This server manages the information for every domain ending in.com. It doesn’t have the final IP address either, but it knows which specific name servers are responsible for thegenfarmer.comdomain. It points the resolver toward those servers. - Querying the Authoritative Name Servers: Finally, the recursive resolver contacts the authoritative name server for
genfarmer.com. This server is the final authority for the domain; it holds the official records. It looks upgenfarmer.comin its files, finds the corresponding IP address, and sends it back to the recursive resolver. - The Return Trip: The recursive resolver receives the IP address and stores it in its cache for a set period (known as the Time-to-Live or TTL) to speed up future requests. It then passes the IP address back to your computer.
- Making the Connection: Your web browser now has the numerical IP address it needs. It sends a request directly to that address, and the server hosting genfarmer.com responds by sending the website’s data, allowing the page to load on your screen.
This intricate, hierarchical dance ensures the system is both resilient and incredibly efficient, preventing any single point of failure from bringing down the entire internet.
The Critical Importance of DNS for Every Internet User
It’s easy to take DNS for granted, but its importance cannot be overstated. Its primary benefit is providing a human-friendly layer to the internet’s technical infrastructure. By abstracting away the complexity of IP addresses, DNS makes the internet accessible and navigable for billions of people.
- Usability and Accessibility: The most obvious impact of DNS is on usability. Memorable domain names are the foundation of branding, marketing, and simple communication. Without them, there would be no easily shareable links, no memorable website addresses, and online navigation would be a tedious task reserved for the technically savvy.
- Reliability and Redundancy: The distributed nature of DNS means it’s incredibly robust. If one name server goes down, others can still handle requests. Furthermore, DNS allows website owners to change their hosting provider (and thus their IP address) without changing their domain name. The DNS records are simply updated, and traffic is seamlessly redirected to the new server, ensuring continuity of service.
- Speed and Performance: Through extensive caching at every level (browser, operating system, recursive resolver), DNS significantly speeds up web browsing. Once a domain has been resolved, the IP address is stored locally for a period, meaning subsequent visits don’t require the full resolution journey, leading to faster page load times.
For professionals in the MMO and digital marketing spaces, a solid understanding of what DNS is and how it works is vital. It influences everything from website performance and SEO to the successful operation of complex automation tools. When you’re managing dozens of accounts, running scripts, or directing traffic, you are relying on DNS to correctly and quickly route every single connection. Delays or misconfigurations in DNS can lead to failed scripts, unreachable services, and lost revenue.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Internet Navigation
The Domain Name System is a foundational pillar of the modern internet. It is a brilliant, decentralized system that works silently to translate the names we remember into the numbers computers need. While it operates out of sight, its role is paramount. For the MMO gamer managing multiple clients, the digital marketer launching a new campaign, or the business owner deploying automated solutions, DNS is the invisible engine ensuring every connection reaches its intended destination swiftly and reliably.
At GenFarmer, we build solutions that operate on the very backbone of this network infrastructure. Our ecosystem—from robust box phone farm hardware and proxy routers that give you control over your network identity, to flexible cloud phone rentals—is designed for professionals who demand flawless connectivity. Our automation solutions, like GenFarmer Trust for account nurturing and GenFarmer Boost for engagement scaling, depend on a sophisticated understanding of network protocols like DNS to deliver real, measurable results.
Ready to harness the full power of the internet’s infrastructure for your operations? Explore the GenFarmer ecosystem and discover how our tools can revolutionize your digital strategy.











