In the constantly evolving age of the Internet, securing personal information and data has become a top concern for every user. The Proxy Server emerged as an effective solution to help hide the real IP address, enable anonymous access, and protect online privacy. Additionally, Proxies offer many practical benefits such as increasing speed, saving bandwidth, securing connections, and expanding access capabilities. Through this article, we will delve into the details of what a Proxy is, its operating principles, classifications, benefits, potential risks, as well as instructions for effective setup and use.
What is a Proxy?
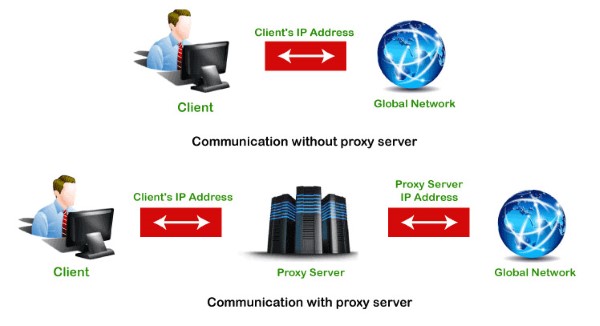
What is a Proxy? A proxy is an intermediary tool between a user and the Internet, acting as a bridge to transmit data and ensure safety during access. A proxy can function as a firewall or a web filter, helping to control and protect user information when using the Internet.
Example of a Proxy: 77.73.0.169:9090. In this example, the Proxy’s IP address is 77.73.0.169, and the access port is 9090.
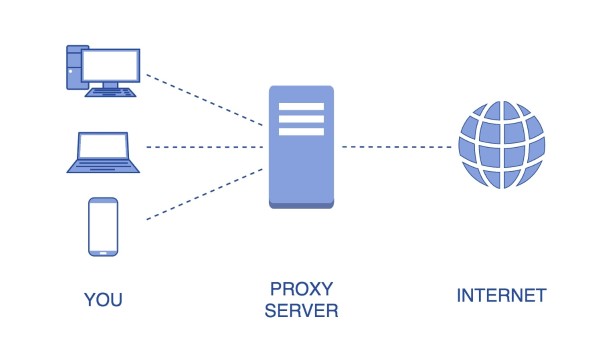
Reasons to use a Proxy Server
In many cases, using a Proxy Server becomes a mandatory requirement or offers significant benefits. Here are some of the main reasons why users use a Proxy:
- Protect privacy and enhance anonymity: A proxy helps hide your real IP address and location, reducing the risk of being tracked or traced online. This allows you to browse the web safely and keep your true identity private.
- Access restricted websites and services: Some websites may block access based on geographical location or impose bans on certain IP addresses. Using a Proxy allows you to change your virtual location and easily bypass these restrictions to access them normally.
- Secure connections and limit the risk of attacks: A proxy acts as a layer of defense, preventing threats from the network. It helps filter malicious content, warn about dangerous websites, block ads, and protect the system from some forms of attacks like DDoS.
- Increase web Browse speed and save bandwidth: A proxy can cache copies of frequently visited websites. This shortens response times, reduces the load on the connection, and provides a smoother experience for the user.
- Manage Internet access in businesses: A proxy allows administrators to control and limit employees’ access rights. They can block inappropriate websites, prevent information leaks, and manage bandwidth usage to optimize work productivity.
Additionally, many users use proxies to access social networks and forums when blocked, share and download documents, or avoid being tracked by website monitoring systems…

Common Types of Proxy Servers Today
There are many ways to classify proxies based on different criteria such as function, level of anonymity, mechanism of operation, etc. Based on the transparency of the Proxy, we can divide them into 4 main types:
Transparent Proxy
A Transparent Proxy is a type of proxy that uses the user’s IP address to authenticate requests to access websites. This type of proxy is often used in public places such as libraries, bookstores, schools, parks, or supermarkets. The advantage of a transparent proxy is its ability to easily control and filter access content by simplifying the process of identifying the server and the client.
Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy works similarly to the incognito Browse mode commonly used for personal purposes. Instead of using your IP address to access a website, an anonymous proxy will hide your real IP and still allow you to access it. This helps protect personal information and leaves no trace on the websites you visit.
Furthermore, Browse through an anonymous proxy also helps reduce the risk of data collection by marketers. As a result, you will encounter fewer ads or annoying marketing campaigns. However, this effectiveness is not always absolute, and sometimes ads may still appear.
Distorting Proxy
This is a type of Anonymous Proxy that can hide the user’s IP address and provide a fake IP address. The destination website, upon receiving the request, will think it comes from a different address and not from the Proxy. However, the destination server still has ways to detect that it is not the real address. A Distorting Proxy adds another layer of protection for the user but is not truly completely anonymous.
High Anonymity Proxy
A high anonymity proxy works by periodically changing your IP address when accessing a website’s server. This makes it more difficult for websites to control and track traffic. Compared to a regular anonymous proxy, a high anonymity proxy provides a superior level of safety and security, helping to protect personal information and maintain privacy while surfing the web.

How a Proxy Server Works
Every computer on the Internet has a unique IP address, similar to your home address. For data to be sent to the right place, the Internet needs to know the IP address of the receiving device, just as the post office needs to know an address to deliver a letter.
A Proxy Server is a special computer on the Internet with its own IP address that your computer recognizes. When you send a web request, it first goes to the Proxy Server. There, the Proxy Server makes the request on your behalf, collects the response from the web server, and then forwards the data so you can view the website’s content in your browser.
In addition to forwarding requests, a Proxy Server can also modify the data before sending it, while still ensuring that the received result is correct. It can change your IP address to hide your real location, enhancing your privacy. A Proxy Server can also encrypt data to improve security during transmission and block access to specific websites based on their IP address.
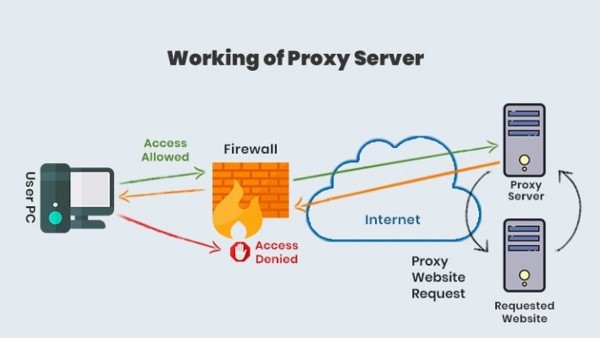
Key Features of a Proxy Server
Modern Proxy Servers offer many outstanding features that not only address common user needs but also open up new and exciting possibilities. Here are the main characteristics and features of a Proxy:
Firewall and Content Filtering
What are the features of a Proxy? A Proxy Server can act as a firewall to protect the internal network from unauthorized access from the internet. By setting the Proxy as a control and transit gateway, network administrators can restrict access from clients and only allow valid connections.
Additionally, a Proxy also has the ability to filter content and block inappropriate websites such as pornographic, violent, or gambling sites. Parents can use a Proxy to prevent their children from accessing harmful content or malicious websites.
Connection Sharing via Proxy Server
Using a Proxy allows multiple users (clients) to share Internet access through a single IP address. The Proxy will receive all requests from the clients and then redirect them to the destination server to get a response.
This mechanism saves on the number of IP addresses needed, reducing costs for businesses that want to provide Internet access to many employees. A typical Proxy Server can serve thousands of clients. However, too many simultaneous connections can also make the Proxy unstable.
Data Storage and Caching
Most websites today have a lot of static content that doesn’t change often, such as logos, images, CSS files, and JavaScript files. A Proxy Server can store this data in its cache and return it to the user quickly without having to reload it from the origin server each time.
When a user sends a request to access a webpage, the Proxy will check if the corresponding content is already in the cache. If it is, it will retrieve the data from the cache and respond immediately. If not, or if the data is outdated, the Proxy will request new data from the origin server and update the cache at the same time.
This mechanism significantly reduces page load times, improves the user experience, reduces the load on the server, and saves bandwidth. Previously visited websites will load much faster than the first time.
The effectiveness of the cache depends on its size and the data update policy. Network administrators can customize the cache size and set the lifespan for each type of content to ensure the information’s freshness and accuracy.

Benefits of Using a Proxy Server
After using it for some time, I have found that a Proxy Server offers several significant benefits:
- Privacy Protection: A Proxy Server allows me to access the Internet anonymously. Some Proxy Servers can also change the IP address and identifying information in outgoing requests. This way, the destination server cannot determine who made the request, helping to protect my personal information and Browse habits.
- Content Management and Control: The Internet has many potential risks, but using a Proxy helps filter and protect the content I access, ensuring greater safety.
- Increased Speed and Bandwidth Savings: A Proxy Server helps improve overall network performance by caching popular websites. This not only speeds up access but also reduces bandwidth consumption.
- Access to Blocked Content: Thanks to its ability to change my IP address and geographical location, a Proxy Server allows me to easily access content that is blocked or restricted by region.
- Security Level of a Proxy Server: To protect my online activities from third-party tracking, I have configured the Proxy Server to encrypt web requests. At the same time, malicious software or websites are also blocked from access through the Proxy, enhancing security. The company where I work also integrates the Proxy Server with a VPN (Virtual Private Network). Users can connect remotely through the company’s Proxy, ensuring data safety. The VPN provides a direct connection channel to the company’s internal network, helping to manage and verify users effectively. As a result, employees can access resources securely, protecting the company’s important information.
Potential Risks When Using a Proxy Server
Every technology has two sides, and Proxy Servers are no exception. Although they offer many benefits, I have also encountered some risks while using them:
- Slow Connection Speed: A proxy can improve loading times for previously cached websites due to its caching feature. However, when accessing new websites, a proxy can significantly reduce connection speed, causing interruptions to the experience.
- Low Stability: Free proxies often lack high performance and are prone to service interruptions or sudden disconnections. This has caused me to spend a lot of time troubleshooting, especially when I’m in the middle of important work.
- Security Limitations: Although a proxy can hide an IP address and bypass firewalls, it doesn’t always guarantee traffic encryption. For example, when I connect to a proxy over a wireless network, the risk of being monitored by others through a VPN or monitoring tools is very high, affecting security.
- Limited Functionality: Proxies often only work at the device level and do not support individual applications. This causes a lot of inconvenience, especially when I need to set up different proxies for specific applications.
Although the risks above do not diminish the value of a Proxy Server, they are factors to consider carefully when choosing and using one.

Should You Use a Proxy Server?
Whether or not to use a Proxy Server depends on the specific needs and purposes of each individual and organization.
Using a Proxy Server is a reasonable choice if you:
- Want to browse anonymously, hide your IP address, and protect your online identity.
- Need to access services or content restricted by geographical location.
- Want to speed up web Browse by using cached data.
- Are concerned about information security when using public networks like free Wi-Fi.
- Want to filter out ads or unwanted content while Browse the web.
- Need to collect data without leaving a trace.
However, you should consider not using a Proxy if:
- You need high reliability and stability in terms of network speed and quality.
- You are conducting sensitive online transactions such as payments or logging into bank accounts.
- You are concerned about the security of your personal information when using a free Proxy.
- You are using services that require accurate IP address verification.
- You need to use applications or features that are not compatible with a Proxy.

Simple Guide to Setting Up a Free Proxy
For casual users, using free Proxy services is a reasonable option to start experiencing. Here is a guide to setting up a Proxy for two popular browsers, Chrome and Firefox:
How to Set Up a Free Proxy on Firefox
Setting up a Free Proxy Server on Firefox is very simple and quick. Here are the steps:
- Step 1: Access Network Settings:
- Open the Firefox browser, click the Menu icon (three horizontal lines at the top right corner).
- Select Settings (Options).
- Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on Connection Settings.
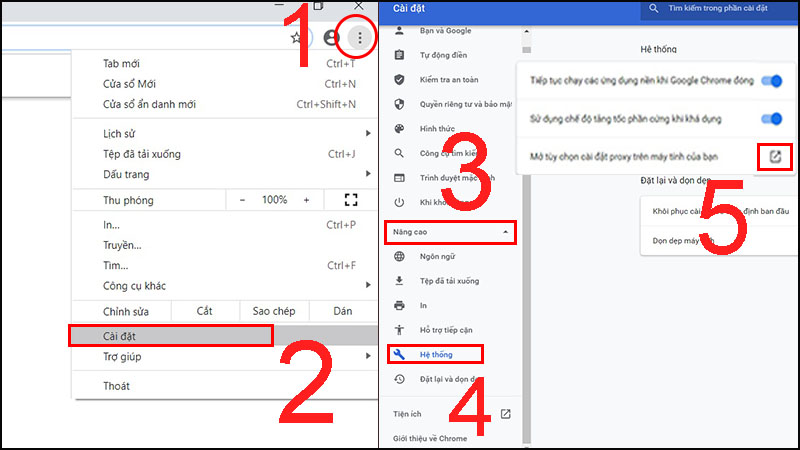
- Step 2: Configure the Proxy:
- In the Connection Settings window, select Manual proxy configuration.
- Fill in the necessary information:
- HTTP Proxy: Enter the IP address and Port of the HTTP Proxy Server.
- HTTPS Proxy: Enter the IP address and Port of the HTTPS Proxy Server if using a secure proxy.
- After completing, click OK to save the settings.
With these steps, you can easily use a Free Proxy on Firefox to improve your connection and enhance security.
Guide to Setting Up a Proxy on Chrome
Here are the detailed steps to set up a Proxy on the Chrome browser:
Step 1: Access Advanced Settings
- Open Chrome, click the three-dot icon (top right corner).
- Select Settings.
- Scroll down and click on Advanced.
- In the System section, select Open your computer’s proxy settings.
Step 2: Set up the Proxy
In the proxy settings window, you can choose between two modes:
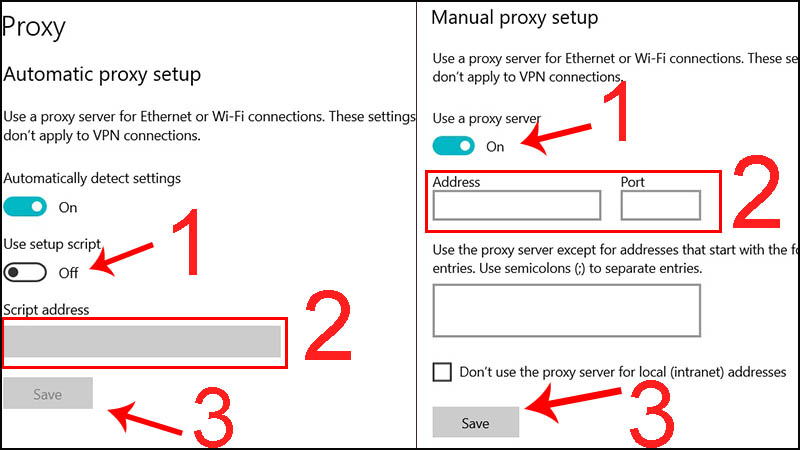
- Automatic proxy setup:
- Turn on the mode by dragging the slider from Off to On.
- Enter the proxy address into the Script address box.
- Click Save to save.
- Manual proxy setup:
- Turn on the mode by dragging the Use a proxy server slider from Off to On.
- Enter the proxy address and port into the corresponding boxes.
- Click Save to finish.
With the steps above, you can easily set up and change the Proxy for the Chrome browser to optimize your connection and protect your privacy.
Comparing Proxy and NAT
Currently, both Proxy and NAT are widely used and have received many positive reviews. So, what is the difference between NAT and a Proxy?
- A Proxy Server often acts as a representative for the user when accessing the system, helping to hide the user’s IP address and control traffic.
- NAT (Network Address Translation) changes the source address of the traffic before the data passes through the NAT and connects to the Internet to reach the destination address.
- A Proxy operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) or higher, while NAT operates at the network layer (Layer 3).
Differentiating Between a VPN and a Proxy?
Just like NAT and Proxy, VPNs are becoming increasingly popular in today’s digital age. So what is the difference between a VPN and a Proxy?
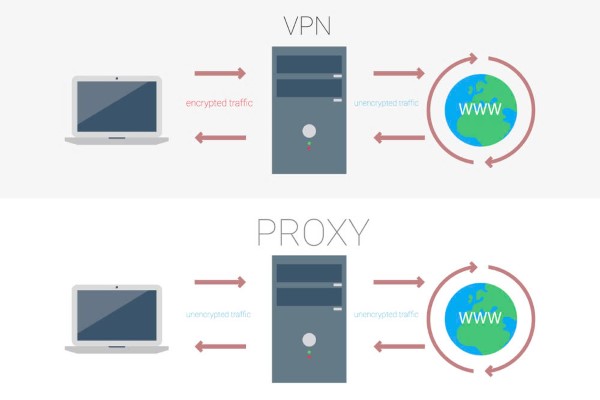
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates encrypted “tunnels,” providing high security features to effectively hide the IP address. When connecting via a VPN Server, all traffic will be encrypted and secured at a complex level, protecting user information from external threats.
- A Proxy, on the other hand, only operates at the browser level and relies on existing security vulnerabilities. A Proxy helps hide the IP address but does not provide as strong security as a VPN. Meanwhile, a VPN applies security to the entire computer system, has a higher level of protection, but often requires users to pay a fee to use all its features.
Conclusion
Hopefully, through this article, you have gained useful knowledge about what a Proxy is and can apply it effectively in your work and digital life.
Furthermore, to automate Phonefarm, Boxphone, Box phone Farm tasks and manage a large number of accounts safely, minimizing the risk of being banned, you can consider the solution from GenFarmer – the number one platform for automating phone farming that supports a wide range of application platforms. Do not hesitate to contact us now to experience how to optimize your work efficiency.











